LU decomposition of a matrix with complete pivoting, and related features. More...
#include <FullPivLU.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | { RowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::ColsAtCompileTime, Options = MatrixType::Options, MaxRowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxColsAtCompileTime } |
| typedef _MatrixType | MatrixType |
| typedef MatrixType::Scalar | Scalar |
| typedef NumTraits< typename MatrixType::Scalar >::Real | RealScalar |
| typedef internal::traits < MatrixType >::StorageKind | StorageKind |
| typedef MatrixType::Index | Index |
| typedef internal::plain_row_type < MatrixType, Index >::type | IntRowVectorType |
| typedef internal::plain_col_type < MatrixType, Index >::type | IntColVectorType |
| typedef PermutationMatrix < ColsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime > | PermutationQType |
| typedef PermutationMatrix < RowsAtCompileTime, MaxRowsAtCompileTime > | PermutationPType |
Public Member Functions | |
| FullPivLU () | |
| Default Constructor. | |
| FullPivLU (Index rows, Index cols) | |
| Default Constructor with memory preallocation. | |
| FullPivLU (const MatrixType &matrix) | |
| FullPivLU & | compute (const MatrixType &matrix) |
| const MatrixType & | matrixLU () const |
| Index | nonzeroPivots () const |
| RealScalar | maxPivot () const |
| const PermutationPType & | permutationP () const |
| const PermutationQType & | permutationQ () const |
| const internal::kernel_retval < FullPivLU > | kernel () const |
| const internal::image_retval < FullPivLU > | image (const MatrixType &originalMatrix) const |
| template<typename Rhs > | |
| const internal::solve_retval < FullPivLU, Rhs > | solve (const MatrixBase< Rhs > &b) const |
| internal::traits< MatrixType > ::Scalar | determinant () const |
| FullPivLU & | setThreshold (const RealScalar &threshold) |
| FullPivLU & | setThreshold (Default_t) |
| RealScalar | threshold () const |
| Index | rank () const |
| Index | dimensionOfKernel () const |
| bool | isInjective () const |
| bool | isSurjective () const |
| bool | isInvertible () const |
| const internal::solve_retval < FullPivLU, typename MatrixType::IdentityReturnType > | inverse () const |
| MatrixType | reconstructedMatrix () const |
| Index | rows () const |
| Index | cols () const |
Protected Attributes | |
| MatrixType | m_lu |
| PermutationPType | m_p |
| PermutationQType | m_q |
| IntColVectorType | m_rowsTranspositions |
| IntRowVectorType | m_colsTranspositions |
| Index | m_det_pq |
| Index | m_nonzero_pivots |
| RealScalar | m_maxpivot |
| RealScalar | m_prescribedThreshold |
| bool | m_isInitialized |
| bool | m_usePrescribedThreshold |
Detailed Description
template<typename _MatrixType>
class FullPivLU< _MatrixType >
LU decomposition of a matrix with complete pivoting, and related features.
- Parameters:
-
MatrixType the type of the matrix of which we are computing the LU decomposition
This class represents a LU decomposition of any matrix, with complete pivoting: the matrix A is decomposed as A = PLUQ where L is unit-lower-triangular, U is upper-triangular, and P and Q are permutation matrices. This is a rank-revealing LU decomposition. The eigenvalues (diagonal coefficients) of U are sorted in such a way that any zeros are at the end.
This decomposition provides the generic approach to solving systems of linear equations, computing the rank, invertibility, inverse, kernel, and determinant.
This LU decomposition is very stable and well tested with large matrices. However there are use cases where the SVD decomposition is inherently more stable and/or flexible. For example, when computing the kernel of a matrix, working with the SVD allows to select the smallest singular values of the matrix, something that the LU decomposition doesn't see.
The data of the LU decomposition can be directly accessed through the methods matrixLU(), permutationP(), permutationQ().
As an exemple, here is how the original matrix can be retrieved:
Output:
Member Typedef Documentation
| typedef internal::plain_col_type<MatrixType, Index>::type FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::IntColVectorType |
Reimplemented in LU< MatrixType >.
| typedef internal::plain_row_type<MatrixType, Index>::type FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::IntRowVectorType |
Reimplemented in LU< MatrixType >.
| typedef _MatrixType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::MatrixType |
| typedef PermutationMatrix<RowsAtCompileTime, MaxRowsAtCompileTime> FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::PermutationPType |
| typedef PermutationMatrix<ColsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime> FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::PermutationQType |
| typedef NumTraits<typename MatrixType::Scalar>::Real FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::RealScalar |
Reimplemented in LU< MatrixType >.
Reimplemented in LU< MatrixType >.
| typedef internal::traits<MatrixType>::StorageKind FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::StorageKind |
Member Enumeration Documentation
| anonymous enum |
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
Default Constructor.
The default constructor is useful in cases in which the user intends to perform decompositions via LU::compute(const MatrixType&).
Default Constructor with memory preallocation.
Like the default constructor but with preallocation of the internal data according to the specified problem size.
- See also:
- FullPivLU()
| FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::FullPivLU | ( | const MatrixType & | matrix | ) |
Constructor.
- Parameters:
-
matrix the matrix of which to compute the LU decomposition. It is required to be nonzero.
Member Function Documentation
| FullPivLU& FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::compute | ( | const MatrixType & | matrix | ) |
| internal::traits<MatrixType>::Scalar FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::determinant | ( | ) | const |
- Returns:
- the determinant of the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition. It has only linear complexity (that is, O(n) where n is the dimension of the square matrix) as the LU decomposition has already been computed.
- Note:
- This is only for square matrices.
- For fixed-size matrices of size up to 4, MatrixBase::determinant() offers optimized paths.
- Warning:
- a determinant can be very big or small, so for matrices of large enough dimension, there is a risk of overflow/underflow.
- See also:
- MatrixBase::determinant()
- Returns:
- the dimension of the kernel of the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition.
- Note:
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
| const internal::image_retval<FullPivLU> FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::image | ( | const MatrixType & | originalMatrix | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- the image of the matrix, also called its column-space. The columns of the returned matrix will form a basis of the kernel.
- Parameters:
-
originalMatrix the original matrix, of which *this is the LU decomposition. The reason why it is needed to pass it here, is that this allows a large optimization, as otherwise this method would need to reconstruct it from the LU decomposition.
- Note:
- If the image has dimension zero, then the returned matrix is a column-vector filled with zeros.
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
Example:
Output:
- See also:
- kernel()
| const internal::solve_retval<FullPivLU,typename MatrixType::IdentityReturnType> FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::inverse | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- the inverse of the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition.
- Note:
- If this matrix is not invertible, the returned matrix has undefined coefficients. Use isInvertible() to first determine whether this matrix is invertible.
- See also:
- MatrixBase::inverse()
| bool FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::isInjective | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- true if the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition represents an injective linear map, i.e. has trivial kernel; false otherwise.
- Note:
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
| bool FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::isInvertible | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- true if the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition is invertible.
- Note:
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
| bool FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::isSurjective | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- true if the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition represents a surjective linear map; false otherwise.
- Note:
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
| const internal::kernel_retval<FullPivLU> FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::kernel | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- the kernel of the matrix, also called its null-space. The columns of the returned matrix will form a basis of the kernel.
- Note:
- If the kernel has dimension zero, then the returned matrix is a column-vector filled with zeros.
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
Example:
Output:
- See also:
- image()
| const MatrixType& FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::matrixLU | ( | ) | const [inline] |
| RealScalar FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::maxPivot | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- the absolute value of the biggest pivot, i.e. the biggest diagonal coefficient of U.
| const PermutationPType& FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::permutationP | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- the permutation matrix P
- See also:
- permutationQ()
| const PermutationQType& FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::permutationQ | ( | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- the permutation matrix Q
- See also:
- permutationP()
- Returns:
- the rank of the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition.
- Note:
- This method has to determine which pivots should be considered nonzero. For that, it uses the threshold value that you can control by calling setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
| MatrixType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::reconstructedMatrix | ( | ) | const |
| FullPivLU& FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::setThreshold | ( | Default_t | ) | [inline] |
Allows to come back to the default behavior, letting Eigen use its default formula for determining the threshold.
You should pass the special object Eigen::Default as parameter here.
lu.setThreshold(Eigen::Default);
See the documentation of setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
| FullPivLU& FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::setThreshold | ( | const RealScalar & | threshold | ) | [inline] |
Allows to prescribe a threshold to be used by certain methods, such as rank(), who need to determine when pivots are to be considered nonzero. This is not used for the LU decomposition itself.
When it needs to get the threshold value, Eigen calls threshold(). By default, this uses a formula to automatically determine a reasonable threshold. Once you have called the present method setThreshold(const RealScalar&), your value is used instead.
- Parameters:
-
threshold The new value to use as the threshold.
A pivot will be considered nonzero if its absolute value is strictly greater than 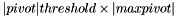 where maxpivot is the biggest pivot.
where maxpivot is the biggest pivot.
If you want to come back to the default behavior, call setThreshold(Default_t)
| const internal::solve_retval<FullPivLU, Rhs> FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::solve | ( | const MatrixBase< Rhs > & | b | ) | const [inline] |
- Returns:
- a solution x to the equation Ax=b, where A is the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition.
- Parameters:
-
b the right-hand-side of the equation to solve. Can be a vector or a matrix, the only requirement in order for the equation to make sense is that b.rows()==A.rows(), where A is the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition.
- Returns:
- a solution.
Example:
Output:
- See also:
- TriangularView::solve(), kernel(), inverse()
| RealScalar FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::threshold | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the threshold that will be used by certain methods such as rank().
See the documentation of setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
Member Data Documentation
IntRowVectorType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_colsTranspositions [protected] |
bool FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_isInitialized [protected] |
MatrixType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_lu [protected] |
RealScalar FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_maxpivot [protected] |
Index FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_nonzero_pivots [protected] |
PermutationPType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_p [protected] |
RealScalar FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_prescribedThreshold [protected] |
PermutationQType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_q [protected] |
IntColVectorType FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_rowsTranspositions [protected] |
bool FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_usePrescribedThreshold [protected] |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- /home/hauberg/Dokumenter/Capture/humim-tracker-0.1/src/ntk/geometry/Eigen/src/LU/FullPivLU.h
 1.7.1
1.7.1